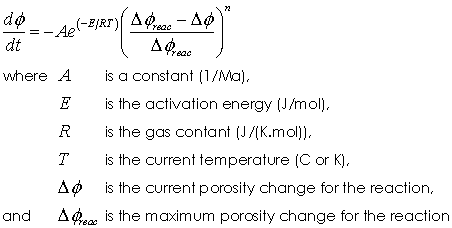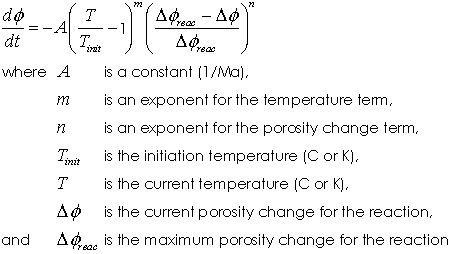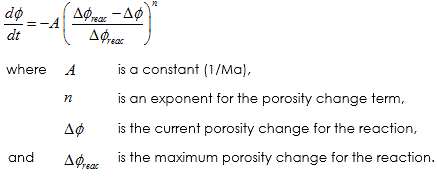Diagenesis_data
Data Structure: Diagenesis_data |
|
Description |
Diagenesis data structure |
Usage |
Diagenesis_data NUM=ival where ival is the data structure number |
Description |
Overview The diagenesis_data structure defines all the properties defining a diagenetic reaction or non-mechanical compaction. The principal features of this model are:
•The non-mechanical compaction reactions are specified individually and then assigned to the material. This facilitates a more concise definition of data and more flexible applications of the models. •Each material may be assigned multiple non-mechanical compaction reactions; e.g. for shallow and deeper events, and the effect of each reaction is accumulative.
The non-mechanical reaction is defined by: •Reaction Model defining the rate of volume reduction and total potential volume reduction. •Compaction Model defining the change of the hardening moduli and pre consolidation pressure. •Cementation Model e.g. defining change in bond strength. •Flow Rule defining whether the volume change is predominantly uniaxial or hydrostatic. •The Maximum porosity change for the reaction.
Notes •Sub-dividing the reaction into several components allows different laws for the reaction, compaction and cementation model to be combined. •An individual diagenesis_data structure is defined for each diagenetic reaction. •The diagenesis_data is assigned to a material by specifying the Diagenesis_assignments keyword on the Material_data structure. •Each material may be assigned more than one diagenetic reaction.
|
| Name Name of diagenesis law |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Name assigned to the diagenesis law (maximum 64 characters)
|
| Reaction_model Diagenesis reaction model number |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
The reaction model defines the rate of volume reduction of the reaction. Two laws are currently implemented: • 1 - The rate of porosity reduction is controlled by an exponential function (see below) • 2 - The rate of porosity reduction is controlled by a power law function (see below) • 3 - The rate of porosity reduction is controlled by a temperature independent power law function (see below) • <100 - User defined laws (used in conjunction with user defined porosity change)
Exponential The rate of porosity reduction in the exponential model is defined by the following equation:
Power Law The rate of porosity reduction in the power law model is defined by the following equation:
Porosity The rate of porosity reduction in the porosity model is defined by the following equation:
Notes •If Reaction_model_name is defined then Reaction_model is set automatically.
|
| Reaction_model_name Diagenesis reaction type |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
The reaction model defines the rate of volume reduction of the reaction. Three laws are currently implemented: • "Exponential" - The rate of porosity reduction is controlled by an exponential function (see below) • "Power Law" - The rate of porosity reduction is controlled by a power law function (see below) • "Porosity" - The rate of porosity reduction is controlled by a temperature independent power law function (see below) • "User_No" - User defined law (used in conjunction with user defined porosity change) where No is the user law number (No > 100)
Exponential The rate of porosity reduction in the exponential model is defined by the following equation:
Power Law The rate of porosity reduction in the power law model is defined by the following equation:
Porosity The rate of porosity reduction in the porosity model is defined by the following equation:
|
| Reaction_properties Properties defining the reaction |
Usage |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Description |
|||||||||||||||
The Diagenesis properties are dependent on the specific law being used and are:
Model 1 - Simple exponential model The exponential model is defined by the equation
This Arrhenius law is based on the model presented by (Wangen, 2000) defines the diagenesis rate to be primarily dependent on the temperature and the percentage of the reaction that has been completed. The total porosity change for the reaction is limited to input maximum value ( Δφchem ). The diagenesis parameters are: • Location 1 - Pre factor constant ( A) • Location 2 - Activation energy ( Q) • Location 3 - Exponent ( n)
Model 2 - Simple power law model The power law model is defined by the equation
The power law defines the diagenesis rate to be primarily dependent on the temperature and the percentage of the reaction that has been completed. The total porosity change for the reaction is limited to input maximum value ( Δφchem ). The diagenesis parameters are: • Location 1 - Pre factor constant ( A) • Location 2 - Exponent ( m) • Location 3 - Initiation temperature ( Tinit) • Location 4 - Exponent ( n)
Model 3 - Temperature-independent power law simple porosity model defined by the equation
The power law defines the diagenesis rate to be dependent on the percentage of the reaction that has been completed. The total porosity change for the reaction is limited to input maximum value ( Δφchem ). The diagenesis parameters are: • Location 1 - Pre factor constant ( A) • Location 2 - Exponent ( n) • Location 3 - Initiation time
|
|||||||||||||||
| Cementation_model_name Cementation model name |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
The valid cementation model types are: • "None" - No additional cementation (default) • "Enhanced_pt" - Specified change in pt • "Cement_yield" - Cementation yield surface
|
| Cementation_properties Properties defining the cementation model |
Usage |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Description |
|||||||||||||||
The cementation properties are dependent on the specific model being used and are:
Model 1 - "Enhanced_pt" The "Pt_increment" model is defined solely by the increment in tensile intercept pt that results from the reaction • Location 1 - Increment in pt ( Δpt)
|
|||||||||||||||
| Compaction_model_name Compaction model name |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
The valid compaction model types are: • "Enhanced_pc" - Porosity loss and increase in pre consolidation pressure ( pc) • "Enhanced_hardening" - Permanent structure characterised by an increase in pre consolidation pressure ( pc) and a reduction in the hardening coefficients defining the normal compression line (ncl), ( λ) and the unloading-reloading line (url), ( κ ). If this model is used then the Hardening_model must be set to type 3 or 4 on the Material_data structure.
|
| Compaction_properties Properties defining the compaction model |
Usage |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Description |
|||||||||||||||
The compaction properties are dependent on the specific law being used and are:
Model 1 - "Enhanced_pc" For this model strength increase due to the reaction is represented by a negative increment of volumetric plastic strain, and hence an increase in the pre consolidation pressure ( pc ). The strength increase is permanent in the sense that a cycle of further positive and negative increment of volumetric plastic strain will return to the same value of ( pc ), and a increase in compression will not diminish this strength increase. Porosity loss and the flow direction must be defined via Maximum_porosity_change and Compaction_direction_factor. The only further consolidation property is the factor of the porosity change for the reaction that contributes to increased strength; i.e. • Location 1 - Factor of porosity contributing to strength increase ( fΔφ) where ( 0.0 ≤ fΔφ ≤ 1.0)
This allows the increase in strength to be limited if application of the full change in volumetric plastic strain results in unrealistic strength increases. Model 2 - "Enhanced_hardening" For this model strength increase due to the reaction is represented by a negative increment of volumetric plastic strain, and hence an increase in the pre consolidation pressure ( pc ), together with a change in either or both the hardening coefficients defining the normal compression line (ncl) ( λ) and the unloading-reloading line (url) ( κ ). The strength increase is permanent in the sense that a cycle of further positive and negative increment of volumetric plastic strain will return to the same value of ( pc ), and a increase in compression will not diminish this strength increase. Porosity loss and the flow direction must be defined via Maximum_porosity_change and Compaction_direction_factor. The consolidation properties are: • Location 1 - Factor of porosity contributing to strength increase ( fΔφ) where ( 0.0 ≤ fΔφ ≤ 1.0 ). This allows the increase in strength to be limited if application of the full change in volumetric plastic strain results in unrealistic strength increases. • Location 2 - The change url hardening constant ( Δκ) where generally ( Δκ) is negative. • Location 3 - The change ncl hardening constant ( Δλ) where generally ( Δλ) is negative.
The Hardening_model must be set to type 4 on the Material_data structure to enable the change in the hardening coefficients to be processed.
|
|||||||||||||||
| Maximum_porosity_change Change in porosity due to reaction |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
The total change in porosity for the reaction (specified as a positive value).
|
| Compaction_direction_factor Compaction direction factor varying from hydrostatic to uniaxial compaction |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Constant defining whether if the compaction is predominantly hydrostatic porosity reduction or uniaxial porosity loss. The factor has a range ( fflow) where ( 0.0 ≤ fflow ≤ 1.0) and 1.0 corresponds to hydrostatic compaction and 0.0 corresponds to uniaxial compaction.
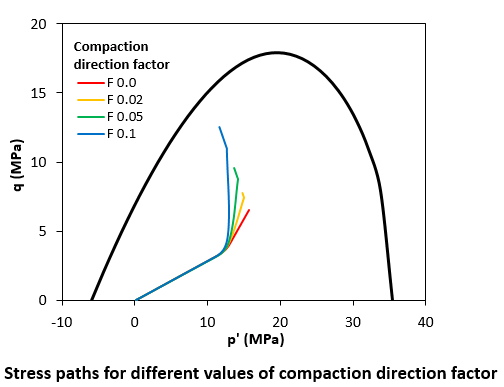
Notes •Note that the compaction direction factor has a strong influence in the stress path evolution. See for example the following plot:
|
| Tension_stress_flag Defines whether the reaction takes place with tension stress states |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Flag to define whether the reaction takes place with tension stress states where • 0 - defines no reaction with tension stress states • 1 - defines that reaction occurs independent of the stress state
The default is dependent on the reaction law and is defined as:
•Model 1 - "Exponential" model (Default: 0 - no reaction with tension stress states) •Model 2 - "Power" model (Default: 0 - no reaction with tension stress states) •Model 3 - "Porosity" model (Default: 1 - reaction with all stress states)
|