GeoInv_001 Concrete Footing Settlement
Problem description
A simplified case of a footing settlement model is considered. Normal loading is prescribed on the top boundary of concrete, which drives downward displacement of the underlying soil. The left and right boundaries of soil are constrained in horizontal direction, whereas the bottom boundary is constrained in vertical direction. The applied normal loading is 20 MPa and is ramped up following S-curve (Curve_type = 2).
In this demonstration, we focus on the data structure in ParaGeoInv data file, instead of the constitutive behaviour of concrete footing settlement. For this reason, we assume only elastic deformation in soil material.
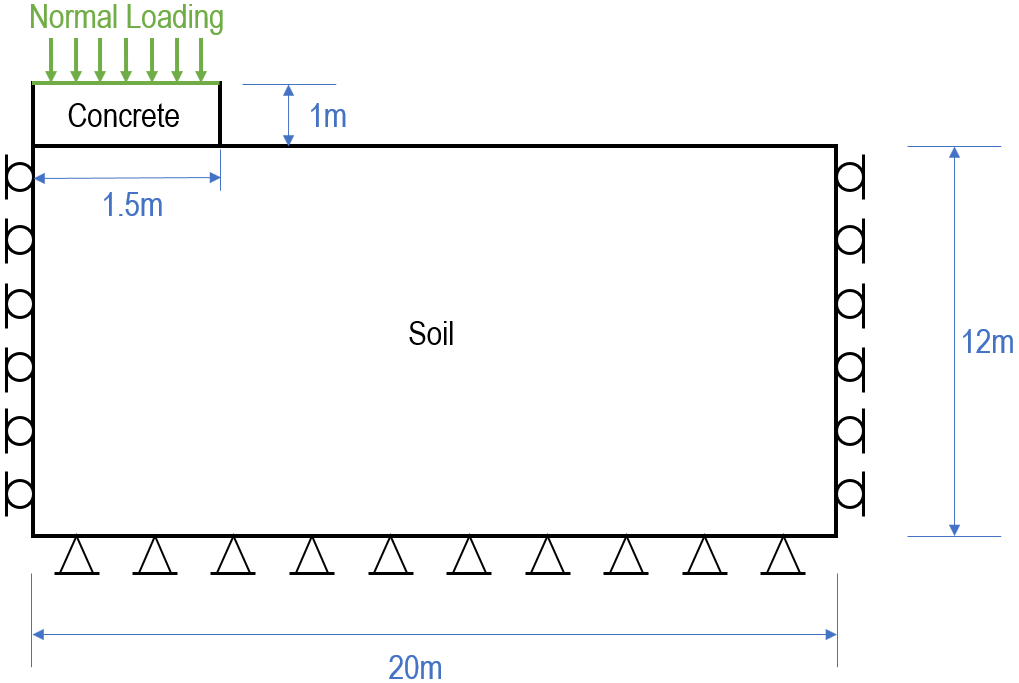
Geometry description and material properties
The purpose of the inverse analysis is to recover Young's modulus of the soil material. The inverse process aims to satisfy a target solution, which in the present case is the time evolution of Displacement Y at a point located on the concrete - soil interface. The target solution and global distribution of Displacement Y are depicted as follows (note that the target solution has been defined via a reference simulation solution).
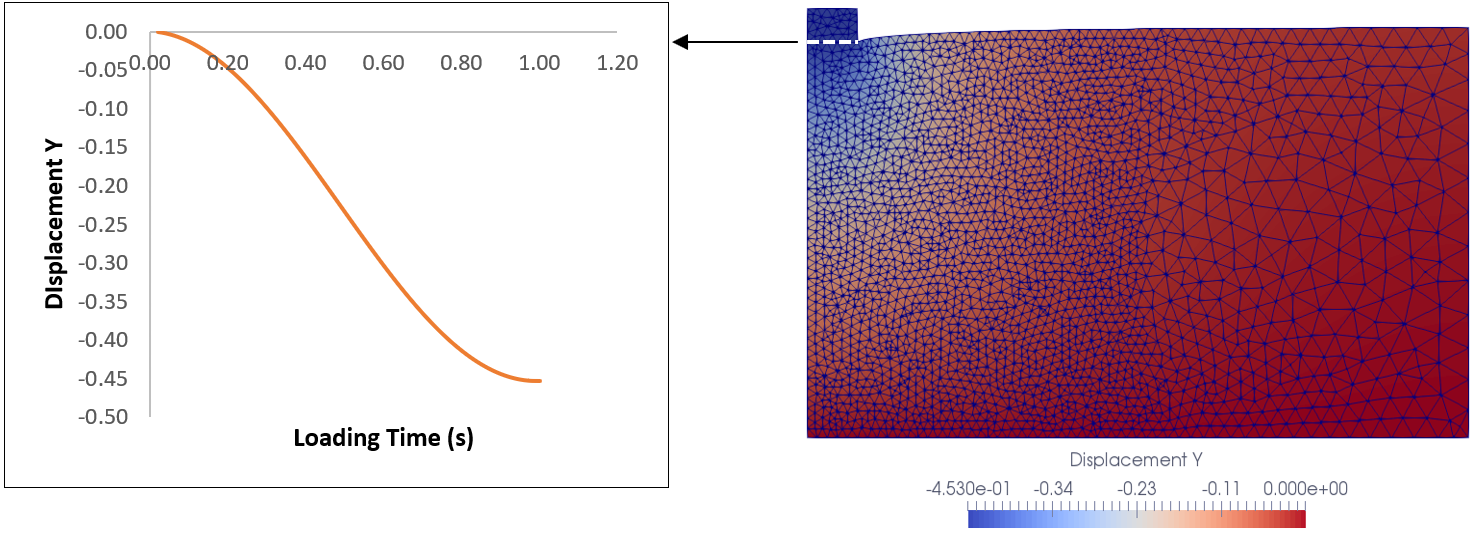
Target solution retrieved from the surface of interest
Note that generally the target solution for an inverse analysis would consist on experimental or field observations. However for demonstrative purposes the target solution for the present tutorial example is generated using a ParaGeo reference simulation with a data file defined following the modelling setup described above. The reference solution is provided in GeoInv_001\Reference_solution. The detailed description of the simulation data file is not provided here as the user is assumed to be already familiar with ParaGeo so the focus in the present tutorial example is made in describing the .inp file for the inverse analysis.
The material properties corresponding to soil and concrete material used to provide the target solution are given in the table below.
|
The outcome of the inverse analysis are evaluated in terms of the evolution of misfit value and comparison between target and optimal solutions.
