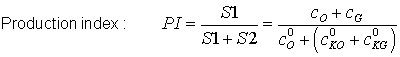Kerogen_kinetics
Data Structure: Kerogen_kinetics |
|
Description |
Defines the assignment and processing data associated with Kerogen_kinetics definition |
Usage |
Kerogen_kinetics NUM=ival where ival is the data structure number |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Overview This data structure defines the assignment and processing data associated with kerogen kinetics.
Screening of potential source rocks is performed by measurement of total organic carbon (TOC) content and Rock-Eval type pyrolysis yield (S1 and S2; sometimes P1 and P2), where:
•S1 = the amount of free hydrocarbons (gas and oil) in the sample. •S2 = the amount of hydrocarbons generated through thermal cracking of non-volatile organic matter.
Reactive kerogen is thermally degradable: it is defined by the pyrolysis S2 yield and when the S2 yield is normalized to the TOC, the ratio is known as the hydrocarbon index (HI)
HI therefore provides an indication of the reactive to inert kerogen proportions in the sedimentary organic matter (SOM).
Hydrocarbon yields are reduced to carbon equivalents using a factor W (e.g. W=0.85 ), which is the weight fraction of carbon in hydrocarbons. However, S1 sometimes is implicitly defined considering W, so that in this case W=1.0 (default value in ParaGeo).
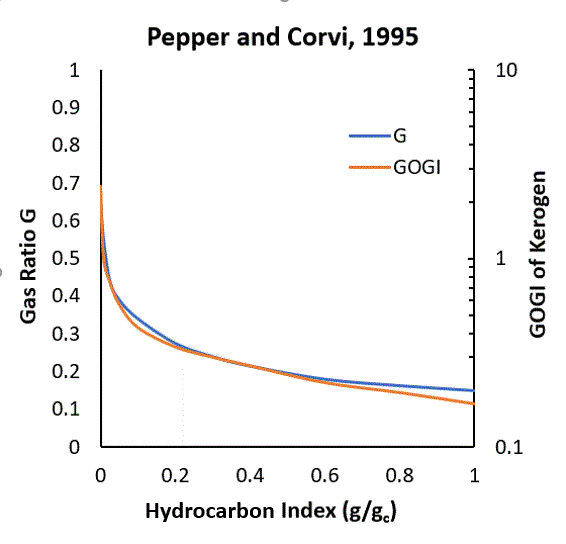
The ratio of gas generated relative to oil ( G) is also defined. G differs from the often used expression ( GOGI ), but they are related (see Pepper and Corvi, 1995 Figure 2) reproduced here.
The equivalent fractional carbon concentrations relative to the initial total carbon mass are then:
and the reactive kerogen is defined as
Key indices and quantities defining the conversion of kerogen to hydrocarbon are:
Note that Transformation ratio TR is also referred to as Transformation index TI in the manual.
Five pre-defined kerogen types are available defined by the organofacies presented by Pepper and Corvi (1995) (see table):
Alternatively user defined kerogen types may be defined using a Gaussian description or tabular definition of weights and activation energies.
Default kerogen - > oil generation kinetic parameters for the pre-multiplier A0, activation energy Emean and the variance σ for the five organofacies presented by Pepper and Corvi (1995a) are listed in the table below:
Default kerogen - > gas generation kinetic parameters for the pre-multiplier A0, activation energy Emean and the variance σ for the five organofacies presented by Pepper and Corvi (1995a) are listed in the table below:
•*Pepper and Corvi (1995a) have deemed the default value of Emean =206.4 kJ/mol unreliable and unrealistic, thus the default is defined as 230.6 KJ/mol based on results calibrated to the reference solution.
Other default parameters in the kerogen kinetics for the five organofacies presented by Pepper and Corvi (1995) are listed in the table below:
•*Note that Transformation ratio TR is also referred to as Transformation index TI in the manual.
References •Pepper, A.S. and Corvi, P.J. Simple kinetic models of petroleum formation. Part I: oil and gas generation from kerogen. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 12(3) 291-319. 1995 •Pepper, A.S., Dodd, T.A. Simple kinetic models of petroleum formation. Part II: oil-gas cracking. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 12(3) 321-340. 1995. •Pepper, A.S. and Corvi, P.J. Simple kinetic models of petroleum formation. Part III: Modelling an open system. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 12(4) 417-452. 1995.
|
| Name Name of kerogen data |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the name of kerogen data (maximum 32 characters).
|
| Kerogen_facies_type Kerogen facies type |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Specifies the type of kerogen facies. Five pre-defined types as defined by Pepper and Corvi (1995a) with the names A, B, C, D/E, F are available. Alternativelly a user defined type may be specified. Consequently, valid values are:
• "A" - Marine, siliceous or Carbonate/evaporite organofacies from marine algae and bacteria. High sulphur content. Possible IFP classification as Type II'S' • "B" - Marine, siliciclastic organofacies from marine algae and bacteria. Moderate sulphur content. Possible IFP classification as Type II • "C" - Lacustrine organofacies from freshwater algae and bacteria. Low sulphur content. Possible IFP classification as Type I • "D/E" - Terrigenous waxy organofacies from higher plant cuticle, resin, ligin and bacteria. Low sulphur content. Possible IFP classification as Type III'H' • "F" - Terrigenous wax poor organofacies originating from ligin. Low sulphur content. Possible IFP classification as Type III/IV • "DefineName" - User defined kerogen organofacies properties via Kerogen_gas_properties and Kerogen_oil_properties
Notes •If a pre-defined type is selected then Kerogen_gas_properties and Kerogen_oil_properties are set by default.
|
| Kerogen_gas_properties Defines the properties for Kerogen->Gas conversion via a Gaussian distribution |
Usage |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Defines the properties for Kerogen->Gas conversion via a Gaussian distribution. The values comprise: •Location 1 - pre-multiplier ( A0) •Location 2 - activation energy ( Emean) •Location 3 - variance ( σ)
Notes •Default parameters are available for specific named kerogen types:
•*Pepper and Corvi (1995a) have deemed the default value of Emean =206.4 kJ/mol unreliable and unrealistic, thus the default is defined as 230.6 KJ/mol based on results calibrated to the reference solution.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kerogen_gas_table Kerogen gas table |
Usage |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Description |
|||||||||||||||
Defines Kerogen->Gas table. The data is provided as a 2-D table where: •Row 1 - List of Kerogen->Gas weights ( CKG (i)) •Row 2 - List activation energy ( Ei)
|
|||||||||||||||
| Kerogen_oil_properties Defines the properties for Kerogen->Oil conversion via a Gaussian distribution |
Usage |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Defines the properties for Kerogen->Oil conversion via a Gaussian distribution. The values comprise: •Location 1 - pre-multiplier ( A0) •Location 2 - activation energy ( Emean) •Location 3 - variance ( σ)
Notes •Default parameters are available for specific named kerogen types:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kerogen_oil_table Kerogen oil table |
Usage |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Description |
|||||||||||||||
Defines Kerogen->Oil table. The data is provided as a 2-D table where: •Row 1 - List of Kerogen->Oil weights ( CKO (i)) •Row 2 - List activation energy ( Ei)
|
|||||||||||||||
| TOC Total organic carbon by weight TOC |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the total organic carbon by weight ( TOC) in terms of the total organic carbon content in mass; i.e. the percentage of the mass of all carbon organic particles relative to the total mass of the rock matrix. It is therefore a concentration value of the generated and expelled petroleum masses using the total rock mass.
|
| Transformation_index Transformation index TI (Also referred to as Transformation ratio TR) |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines Transformation index ( TI =S1/TOC) in SI units ( ghc /gc) as opposed to the often used units ( mghc /gc ).
|
| Hydrocarbon_index Initial hydrocarbon index (HI) |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines Hydrocarbon index ( HI =S2/TOC) in SI units ( ghc /gc) as opposed to the often used units ( mghc /gc ). Note that Transformation index TI is also referred to as Transformation ratio TR in the manual.
|
| Gas_concentration Gas concentration ratio |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the initial gas concentration ratio ( G ). Valid range is 0.0 < = G < = 1.0, where 0.0 corresponds to Oil-only generation and 1.0 corresponds to Gas-only generation. The gas concentration ratio differs from the often used expression ( GOGI ), but they are related (see Pepper and Corvi, 1995 Figure 2).
|
| Reactive_content Mass of reactive kerogen |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Mass of reactive kerogen CKR defines the initial mass of reactive kerogen terms of the percentage of the reactive mass of all carbon organic particles relative to the total mass of the rock matrix.
|
| Weight_fraction_carbon The weight fraction of carbon in hydrocarbons W |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
W defines the weight fraction of carbon in hydrocarbons (Default 1.0 - corresponding to implicitly including W in S1 and S2).
|
| Thickness Thickness of kerogen layer |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the thickness of kerogen layer. If Thickness is not defined, then the computed element volume will be used.
|
| Kerogen_reaction_count Kerogen reaction count |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the number of parallel reactions in update procedure (Default =11).
|
| Universal_gas_constant Defines the universal gas constant R |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the universal gas constant R (Default: 0.00831446261815324 kJ/K/mol).
|
| Kerogen_density Defines the density of kerogen |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines the density of kerogen (in the range of 1250 kg/m^3).
|
| Hydrocarbon_density_model Hydrocarbon density type |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Hydrocarbon_density_model defines the model for evaluation of the density of the expelled hydrocarbon; i.e. the average density of the expelled oil and liquid gas. Valid values are:
• "Constant" - Constant hydrocarbon density
|
| Hydrocarbon_density_properties Density of combined oil and liquid gas |
Usage |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Description |
|||||||||||||||
Hydrocarbon_density_properties defines density of expelled combined oil and liquid gas. The properties are dependent on the model type:
Constant • Hydrocarbon density - Constant value for hydrocarbon density
Notes •Default hydrocarbon densities are available for specific named kerogen types:
|
|||||||||||||||
| Kerogen_initialisation_flag Defines whether groups assigned kerogen are initialised as kerogen present or not. |
Usage |
||||
|
||||
Description |
||||
Defines whether groups assigned kerogen are initialised as kerogen present or not. By default the kerogen is assigned to the complete group, whereas if set as off then kerogen must be assigned via spatial state initialisation. Valid values are: •0 - kerogen is not present •1 - kerogen is present (default)
|