Abaq_Mech_001 Mechanical Analysis Introduction
This example is provides a simple introduction to performing 2-D mechanical analysis using an explicit dynamic solver. Both dynamic and quasi-static cases are considered, and the methodology for obtaining quasi-static solutions using an explicit solver is demonstrated. Specific issues considered are:
1Problem set up for elastic simulation; i.e. material, prescribing displacement (support_data), surface loading, etc.
2Defining solution parameters.
3Obtaining steady state solutions using an explicit dynamic solver; i.e.
(a) Defining appropriate load curves
(b) Damping
(c) Monitoring the solution using high definition history
The problem consists of a 10m high by 1m wide elastic sandstone column. Uniaxial deformation is enforced by prescribing the horizontal displacement of the column sides and a 10 MPa surface load is applied to the top of the column. As an explicit dynamic solver is used the solution is time dependent and the surface load is prescribed with a time curve that defines its magnitude as a function of time. Several different time curves are considered including a linear ramp, S-Curve and an instantaneous load.
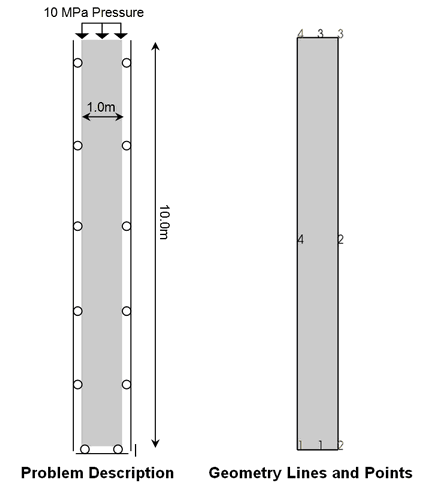
The data file and geometry definition are described in Case 1A Base Case Description.
Simulation Cases
Case 1B Scaling Time for 100 Steps
Case 1C Scaling Time for 1000 Steps
