Rest_001 Restoration of a fold
This tutorial example aims to demonstrate how to perform a geomechanical-based restoration in ParaGeo which is performed by:
1Defining a restoration surface (which can be flat or curved)
2Prescribing vertical displacement on the current model top surface to unfold it and make it to coincide with the restoration surface
3Assuming elastic constitutive relationships for the sediments
4Optionally incorporate plastic models to allow for bedding plane slip
5Representing faults as frictionless contact surfaces
6Optionally considering a de-compaction law following a prescribed porosity trend for the de-burial of the sediment
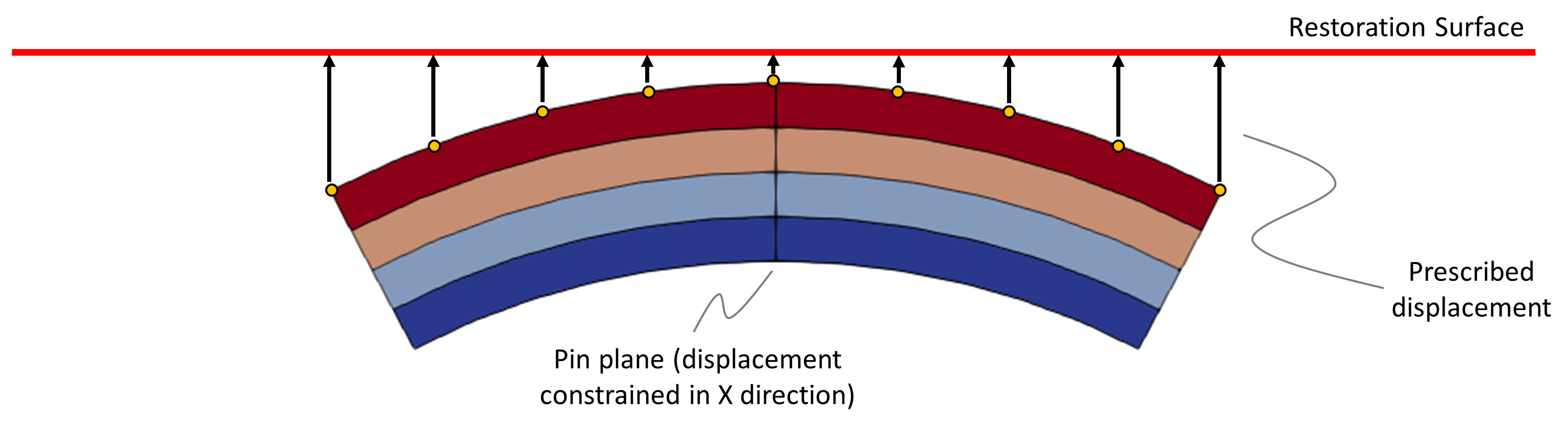
View of the model geometry
The example consists of a 2D fold geometry comprising 4 formations. The model dimensions are approximately 14 km long and 4.3 km high. The pin location (displacement constrained in the X direction) is defined at the fold axis plane.
Specific issues considered in this tutorial example are:
1Set up of a geomechanical restoration in ParaGeo
2Consider a decompaction law during restoration
3Consider intra-formation bedding plane slip
4Add additional constraints to the top surface bed length
Simulation Cases
Case2 Restoration with Bedding Plane Slip
Case3 Restoration with decompaction (synchronous)
Case4 Force-based bed length constraint (high stiffness)
Case5 Force-based bed length constraint (low stiffness)
Case6 Displacement-based bed length preservation
