Stratigraphy Data
In ParaGeo geology-related problems each group corresponds to a different formation/stratigraphic unit and conversely each stratigraphic unit is defined by a single group. Definition of stratigraphy in ParaGeo is required for:
1.Problems where depth computation need to be performed (e.g. problems where geostatic data is used). For such problems the minimum data required corresponds to the identification of the top surface horizon.
2.Evolutionary models with sedimentation/erosion. In such problems the minimum data required is the definition of the stratigraphic sequence from the initial geometry in depositional order (shown below) via identification of the corresponding stratigraphy horizons (top of each stratigraphic unit). It is recommended that the stratigraphy horizons are named identical to their corresponding groups which simplifies the data definition and facilitates referencing.
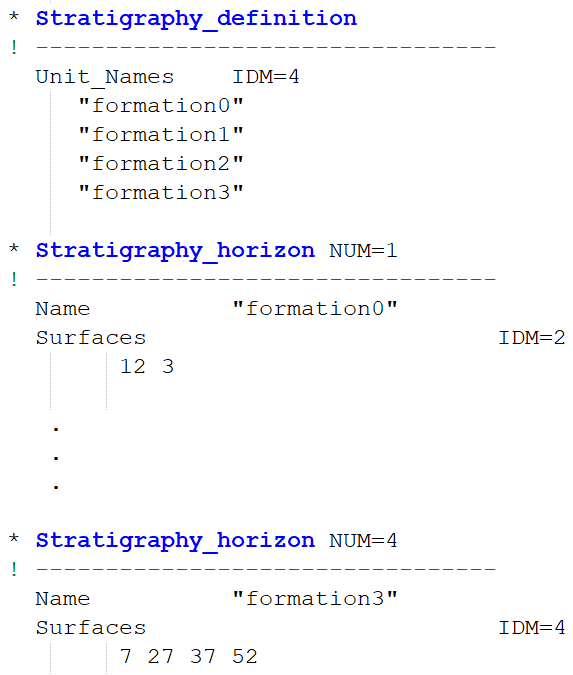
Example of typical stratigraphy definition in a ParaGeo 3D problem
It should be noted that stratigraphy horizons need to be defined continuous across the whole model even if a given formation/group does not cover completely the previous deposited formation (see the picture below).
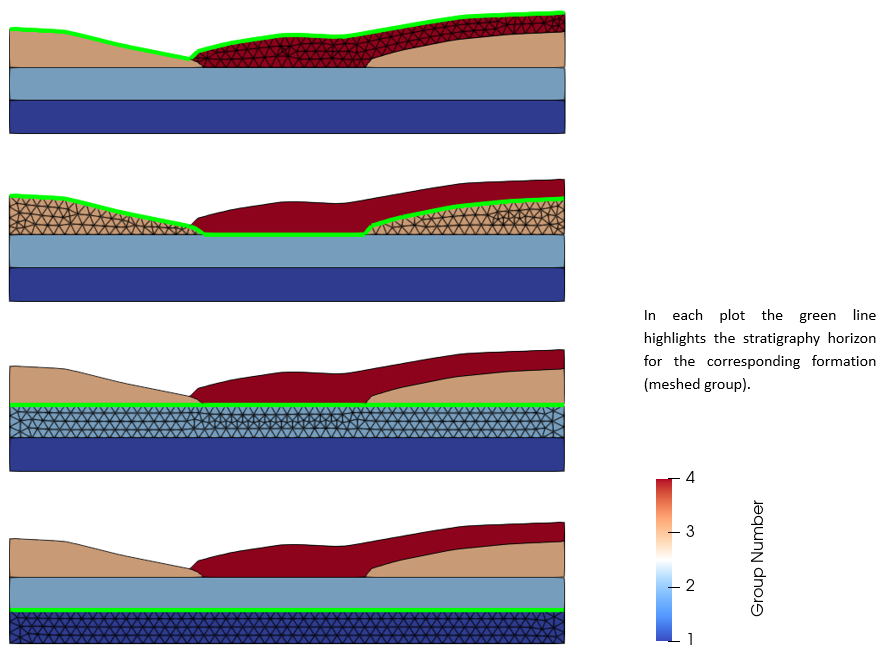
Example of a geometry with 4 ParaGeo groups (formations) defined with 5 surfaces. The green line indicates the stratigraphy horizon corresponding to each formation (meshed group).
Note that definition of stratigraphy allows to use Stratigraphy_surface_load and Stratigraphy_basal_load to apply boundary conditions to the top surface and basal boundary of the model respectively. Such data structures are generally used in evolutionary models where the target geometry entities with a top surface boundary condition are updated when there is sedimentation or erosion.
Data structures relevant to stratigraphy definition / stratigraphy-related operations described in this section of the reference manual are:
•Stratigraphy_horizon defining the geometry entities or geometry set that constitute a stratigraphic surface.
•Stratigraphy_definition defining the stratigraphic sequence in depositional order (from old to young formations), basal horizon, etc.
•Stratigraphy_surface_load defining boundary conditions for the top stratigraphic unit.
•Stratigraphy_basal_load defining boundary conditions for the basal horizon of the model.
•Stratigraphy_smoothing defining conditions for the stratigraphy smoothing algorithm used to smooth sharp angles in any stratigraphy horizon (mainly used to stabilize top surface).
•Stratigraphy_pinchout_data defining conditions for removal of thin, large stratigraphic unit edges pinching out which may lead to numerical stability issues (e.g. in the flanks of a mini-basin).
•Geometry_point_merge defining conditions for elimination of short lines at the edge of stratigraphy units.
Examples
Suggested tutorial examples demonstrating definition of stratigraphy data are:
Mech_002: Uniaxial burial of 2000m of sediment
Geost_002: Staged initialization of a graben
